Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of complex plastic parts with high precision and efficiency. However, as products become more sophisticated and quality expectations rise, traditional trial-and-error design approaches are no longer sufficient. This is where mold flow analysis (also known as mold flow simulatio) plays a critical role, allowing engineers to virtually simulate and optimize the behavior of molten plastic within a mold before physical tooling begins.
What is Mold Flow Analysis?
Mold flow analysis is a computer-aided engineering (CAE) simulation technique used to simulate the flow of molten plastic inside a mold cavity during the injection molding process. Using advanced software, engineers can predict how materials will fill, cool, and solidify inside the mold based on parameters like resin type, melt temperature, gate locations, and cooling design.
The goal of mold flow analysis is to anticipate potential issues early, such as incomplete filling, air traps, weld lines, or warpage, and provide actionable insights that optimize both part and tool design before costly mold fabrication and production begin.
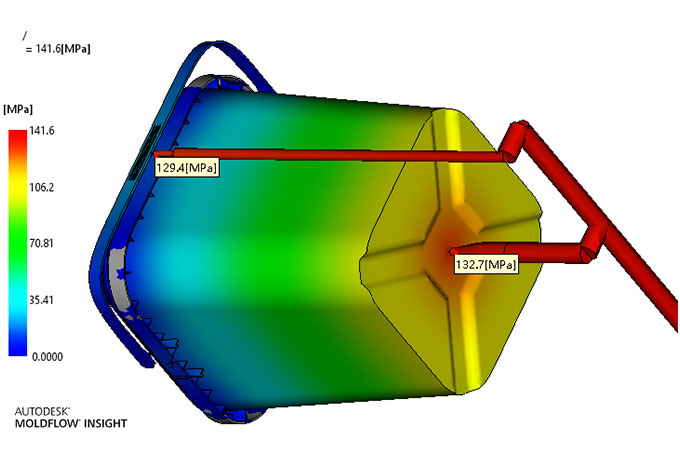
Why Mold Flow Analysis Matters?
1. Early Detection of Defects and Design Flaws
One of the most significant advantages of mold flow analysis is its ability to identify potential defects before physical tooling is made. By simulating how molten plastic enters and fills the cavity, engineers can spot issues such as short shots, air traps, sink marks, or weld lines — all of which can compromise product quality if left unaddressed. [1]
For example, weld lines, which occur where two flow fronts meet, can weaken a part structurally and visually. Flow simulation software helps engineers identify these lines early and reposition gates or adjust wall thickness to minimize their impact.
2. Optimizing Mold and Part Design
Mold flow analysis is an integral part of design for manufacturability (DFM). By simulating the injection molding process virtually, designers can make informed decisions about:
Gate placement: Optimal gate locations ensure balanced flow and reduce defects like air traps and pressure imbalances.
Runner and cooling layout: Simulating how the resin flows and cools allows engineers to design efficient runner systems and cooling channels that reduce cycle times and part stress.
Wall thickness distribution: With simulation, areas prone to sink marks or warpage due to uneven thick regions can be corrected early in the design phase.
This preemptive design refinement not only improves product quality but also reduces costly revisions during physical prototyping, tooling, and production.
3. Material and Process Optimization
Mold flow analysis helps engineers evaluate how different materials will behave in a given design. Different plastics have different melt flow behaviors, viscosity, and cooling characteristics. By testing multiple materials in the simulation software, designers can choose the best candidate based on performance, cost, and processing feasibility.
Furthermore, simulation can explore optimal processing parameters, including injection pressure, melt temperature, and holding pressure, enabling process engineers to refine settings that yield consistent and high-quality parts before physical trials.
4. Reduced Development Time and Cost
Traditional mold design often relies on iterative physical prototyping and trial runs, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive. By employing mold flow simulation early in the design cycle, potential problems can be identified and resolved digitally, reducing the number of costly mold changes and shortening time to market.
In many cases, companies report that mold flow analysis reduces overall development lead time by as much as 20–30% and material usage by 10–15%, while cutting defect rates significantly. [2]
How Mold Flow Analysis Works?
Mold flow analysis uses specialized software to model the injection molding process. Here’s a general overview of how it works:
1. Prepare the 3D Part and Mold Geometry
The analysis begins with the 3D CAD model of the part and the proposed mold, including cavities, gates, runners, and cooling channels. Accurate geometry is essential for valid simulation results.
2. Select Material and Process Parameters
The next step is to input relevant injection molding raw material data, including rheological and thermal properties of the selected plastic resin. Melt temperature, mold temperature, injection speed, and holding pressure are typical process parameters defined before the simulation.
3. Run Virtual Simulation
Once set up, the software runs multiple simulations that may include:
Filling phase: Shows how the molten plastic fills the cavity and highlights potential issues like short shots or uneven flow. [3]
Flow analysis: Evaluates the flow front behavior and how it interacts with mold geometry and obstacles.
Cooling analysis: Predicts cooling rates and temperature distribution during solidification.
Warpage analysis: Identifies potential deformations due to non-uniform cooling and shrinkage.
The combined results help engineers visualize where redesigns or adjustments are needed.
Mold Flow Analysis Benefits in Injection Molding
Improved Part Quality
Mold flow analysis enhances part quality by predicting and preventing defects such as weld lines, air traps, sink marks, and warpage. By viewing simulated flow results, designers can refine part geometry and mold design to avoid these defects before tooling fabrication.
For aesthetic or critical tolerance parts, the ability to optimize gate locations and cooling channels directly translates into better surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and structural integrity.
Cost Savings and Reduced Waste
By uncovering issues early, engineering teams avoid costly revisions and prototype iterations. Mold flow simulation often leads to fewer physical trials and less wasted material in prototyping and production, which both lower tooling and production costs.
In some cases, simulations allow for material reduction and efficient runner system designs, further reducing plastic consumption and waste.
Faster Time to Market
Accelerating the design cycle by resolving flow and cooling issues early enables faster tooling release and production ramp-up. Manufacturers can bring products to market quicker, giving them a competitive edge, especially in industries with rapid product cycles like consumer electronics or automotive.
Optimized Processing Conditions
Mold flow analysis provides valuable insights for determining optimal processing conditions. By evaluating pressure distribution and flow behavior, engineers can fine-tune injection pressure, filling time, and packing settings to ensure consistent quality during production.
Common Mold Flow Analysis Applications
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
By employing mold flow simulation early, designers align part design with moldability requirements, ensuring the final design can be manufactured with minimal defects and cost.
Material Evaluation and Selection
Simulating multiple materials helps select the best resin based on flow characteristics and potential shrinkage or warpage behavior, crucial for parts with thin walls or complex features.
Cooling System Optimization
Since cooling is a major contributor to cycle time, optimizing cooling channel placement and design using simulation can significantly reduce cycle times and improve dimensional stability.
Process Parameter Troubleshooting
Simulation data helps troubleshoot production issues such as flash, short shots, or inconsistent quality by revisiting proposed gate locations, injection speeds, or pressure settings virtually rather than physically.
Mold flow analysis is a powerful tool in modern injection molding that transforms traditional mold design into a data-driven engineering process. By simulating material flow, cooling, and solidification, mold flow analysis helps engineers anticipate issues, optimize designs, improve part quality, reduce costs, and accelerate time to market. Whether used for gating and cooling optimization, material selection, or defect prediction, this simulation technology is increasingly indispensable in competitive injection molding environments.
If you are involved in part or mold design, investing in mold flow analysis as part of your injection mold engineering workflow not only enhances manufacturability but also elevates product performance and reliability. For further services and design assistance, companies often offer dedicated moldflow analysis services integrated with mold and part engineering support.
Reference:
[1] https://news.ewmfg.com/blog/mold-flow-analysis-can-save-your-plastic-injection-mold-design
[2] https://moldneo.com/mold-flow-analysis/
[3] https://www.protolabs.com/resources/design-tips/using-mold-flow-analysis-to-improve-injection-molding-design/











